
This metric is based on tangible assets and does not account for intangible factors like trial balance brand value, intellectual property, or future growth potential. The SE ratio measures the proportion of a company's total assets financed by SE (rather than debt). Long-term liabilities, also known as non-current liabilities, are financial obligations that are due beyond one year or the normal operating cycle of the company. These liabilities are used to finance long-term investments and operations, such as purchasing property, plant, and equipment. Higher ROE metrics relative to comparable companies imply increased value creation using less equity capital, which is precisely what equity investors pursue when evaluating investments.

Limits of the Accounting Equation
Book value per share (BVPS) represents the value available to common shareholders divided by the total number of outstanding shares in a company. Typically, a company will use its retained earnings to finance its operations, keep a working capital reserve, purchase equipment or assets, pay back debt and pay for ongoing business operations and needs. The more a company receives cash from equity investors, the more the share capital account will increase. Banks, investors, venture capitalists and other stakeholders may look at the company’s share equity along with other metrics to evaluate a company’s overall financial health. Finally, the ratio includes some variations on its composition, and there may be some disagreements between analysts. With net income in the numerator, Return on Equity (ROE) looks at the firm’s bottom line to gauge overall profitability for the firm’s owners and investors.

Shareholders’ Equity vs Market Cap
In the case of an acquisition, it is the value of company sales minus any liabilities owed by the company that are not transferred with the sale. The balance sheet always balances out but the accounting equation can’t tell investors how well a company is performing. Assets represent the valuable resources controlled by a company and liabilities represent its obligations. Both liabilities and shareholders’ equity detail how the assets of a company are financed. It will show as a liability if it’s financed through debt but in shareholders' equity if it’s financed through issuing equity Bookkeeping for Veterinarians shares to investors. The concept of shareholders' equity arises from the need to account for the ownership interest in a corporation.
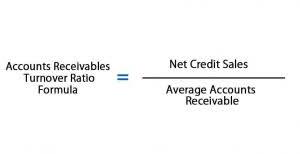
Calculation Formula
- Aside from stock (common, preferred, and treasury) components, the SE statement includes retained earnings, unrealized gains and losses, and contributed (additional paid-up) capital.
- At that time, XYZ Ltd. had $7 billion in total shareholders' equity (or assets minus liabilities).
- It represents proof of a company’s ability to efficiently use capital and execute thoughtful strategic decisions.
- As per the formula above, you'll need to find the total assets and total liabilities to determine the value of a company's equity.
- By comparing total equity to total assets belonging to a company, the shareholders equity ratio is thus a measure of the proportion of a company’s asset base financed via equity.
Here we also provide you with ROSE Calculator with a downloadable excel template. Return on equity jumped significantly because of the decrease in Shareholder's Equity in 2015. Shareholder's equity decreased due to share buyback and accumulated losses that flow through the Shareholder's Equity. In addition, the reluctance to raise debt can cause the company to miss out on growth opportunities to fund expansion plans, as well as not benefit from the “tax shield” from interest expense. The guidelines for what constitutes a “good” proprietary ratio are industry-specific and are also affected by the company’s fundamentals. Of course, the ratio is inadequate to understand the fundamentals of a company and should be evaluated in conjunction with other metrics.
- Therefore, the fact that the company requires fewer funds to produce more output can lead to more favorable terms, especially in early-stage companies and start-ups.
- A firm typically can raise capital by issuing debt (in the form of a loan or via bonds) or equity (by selling stock).
- From the beginning balance, we’ll add the net income of $40,000 for the current period, and then subtract the $2,500 in dividends distributed to common shareholders.
- At the end of 2021, the company reported the following carrying values on its balance sheet.
- Buybacks, for example, can push stockholders’ equity into negative territory in the short term but benefit the company financially in the long run.
Stockholders' Equity: What It Is, How to Calculate It, Example
The resulting figure shows the portion of a company’s equity that is backed by tangible, physical assets. This is the sum that remains for the benefit of the company's shareholders after all liabilities have been subtracted from the assets. It represents the total profits that have been saved and put aside or “retained” for future use. Return on equity or average equity refers to the return it generates from the net income and shareholders' equity.

Next, we’re going to go over the components of the second formula (Common Shares + Preferred Shares + Paid-In Capital + Retained Earnings). First, we’ll go over the components of the first formula (Assets - Liabilities). Across the same time span, Company B’s ROE increased from total shareholders equity formula 15.9% to 20.2%, despite the fact that the amount of net income generated was the same amount. Each year, net income is growing by $2m for both companies, so net income reaches $28m by the end of the forecast in Year 5. Company A has an ROE of 40% ($240m ÷ $600m), but Company B has an ROE of 30% ($240m ÷ $800m), with the lower ROE % being due to the 2nd company carrying less debt on its B/S.
Shareholders’ Equity
- Shareholders’ equity refers to the owners’ claim on the assets of a company after debts have been settled.
- Shareholders' equity isn't the sole indicator of a company's financial health, however.
- This measure excludes treasury shares, which are stock shares owned by the company itself.
- That is, it indicates how much money would be available to the company's shareholders if it goes bankrupt and is forced to pay all of its liabilities.
- DuPont analysis is covered in detail in CFI’s Financial Analysis Fundamentals Course.
A higher SE ratio indicates that a greater portion of the company's assets are financed by equity, suggesting lower financial risk and potentially greater financial stability. Treasury stock does not carry voting rights, nor does it receive dividends, and it is not included in the calculation of earnings per share (EPS). Preferred stocks and preferred shares refer to the same thing—they are interchangeable terms. SE provides a full snapshot of a company's financial health and performance, and it indicates the company’s financial stability. In conclusion, the ROE metric can be an informative metric for investors in assessing management’s ability to efficiently use investor capital to achieve excess profits (and increased returns).
- CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation.
- Determine the company's shareholder equity based on the provided information.
- This helps stakeholders understand how profits are retained, dividends are distributed, and equity capital is managed, thereby facilitating informed investment and management decisions.
- For a homeowner, equity would be the value of the home less any outstanding mortgage debt or liens.
- “Equity” is the net value of an asset once all debt or liabilities on the asset are deducted or taken out of consideration.
- It is obtained by taking the net income of the business divided by the shareholders’ equity.
Balance sheets, like all financial statements, will have minor differences between organizations and industries. However, there are several “buckets” and line items that are almost always included in common balance sheets. We briefly go through commonly found line items under Current Assets, Long-Term Assets, Current Liabilities, Long-term Liabilities, and Equity. As far as limitations go, there are a few, starting with the fact that certain assets may not show up on a balance sheet.

What Are the 3 Elements of the Accounting Equation?
Shareholders’ equity is significantly influenced by the total number of outstanding common shares of a firm, including restricted shares allocated to insiders, corporate officers, and the general public. The sum recorded is based not on the current market value but rather the par value of the common and preferred stock sold by the corporation. When a firm issues common shares and preferred shares in addition to its retained operating profits, this is referred to as shareholder equity, stockholder equity, or shareholder net worth. For instance, in looking at a company, an investor might use shareholders’ equity as a benchmark for determining whether a particular purchase price is expensive. On the other hand, an investor might feel comfortable buying shares in a relatively weak business as long as the price they pay is sufficiently low relative to its equity. Equity, as we have seen, has various meanings but usually represents ownership in an asset or a company, such as stockholders owning equity in a company.